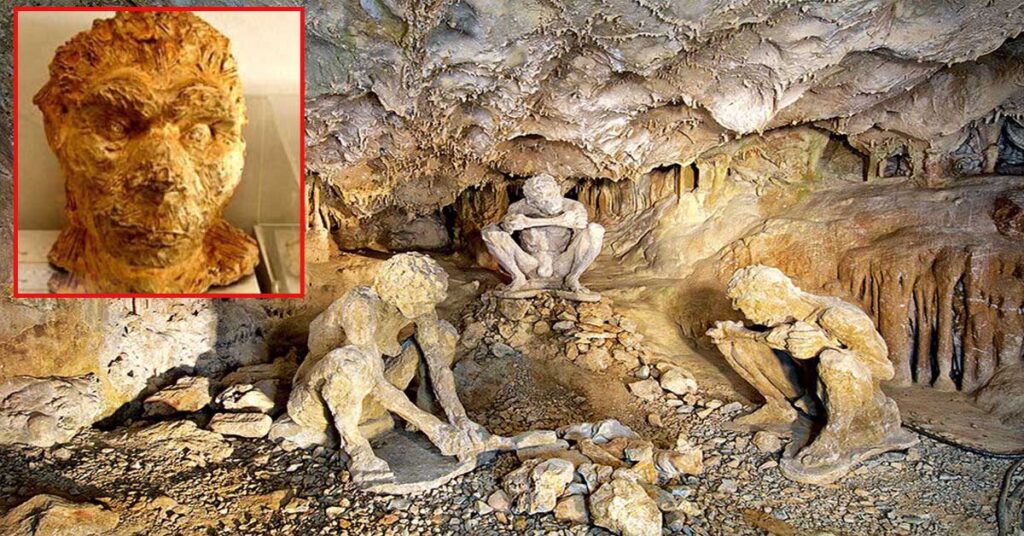
Greece is a land rich in history, where ancient ruins and artifacts offer glimpses into the lives of our ancestors. But hidden beneath the surface lies an even more remarkable treasure – the Petralona Cave, a natural wonder that has captivated the scientific community for decades. This remarkable cavern, formed over a million years ago, has become known as the “Parthenon of paleontology” due to its incredible wealth of fossils and the groundbreaking discovery of the oldest human remains ever found in Greece.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating history and significance of the Petralona Cave, exploring the geological and paleontological wonders that have made it a true gem of Greece’s natural heritage. From the intricate cave formations to the remarkable fossil finds, we’ll uncover the secrets that this ancient site holds, and discover how it is shaping our understanding of human evolution.
The Discovery of the Petralona Cave
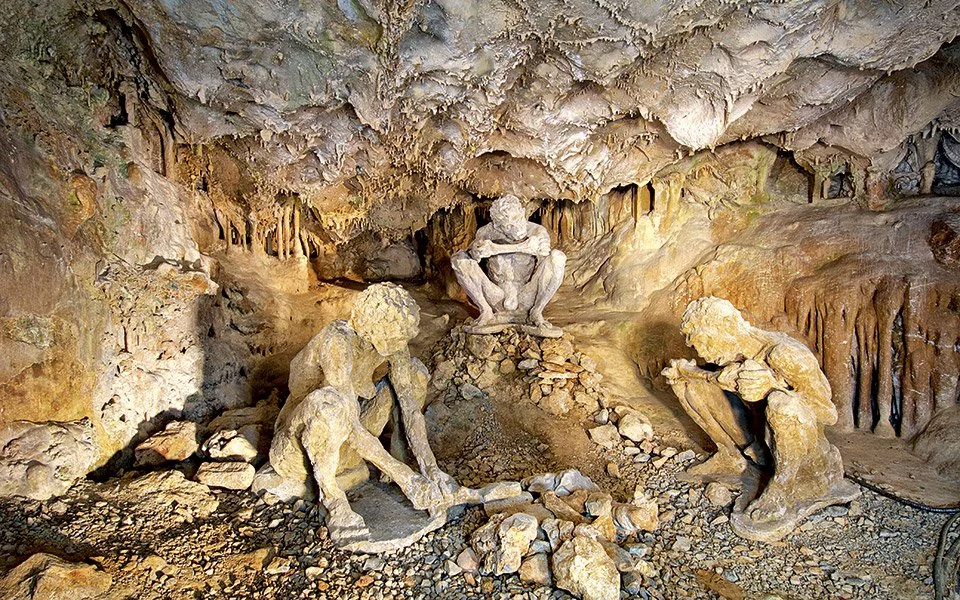

The Petralona Cave was first discovered by local residents of the nearby settlement in 1959. Initially, they made a small opening at the base of Katsika Hill, lowering themselves down by rope to explore the strange hole. What they discovered inside would captivate the scientific community and forever change our understanding of Greece’s prehistoric past.
As the residents descended into the cave, they came across a treasure trove of petrified animal teeth and bones, which they promptly presented to Professor Petros Kokkoros of Thessaloniki’s Aristotle University. Recognizing the significance of the discovery, Greek scientists began excavating the site, revealing a vast network of passages and gathering a wealth of artifacts.
The Geological Wonders of the Petralona Cave

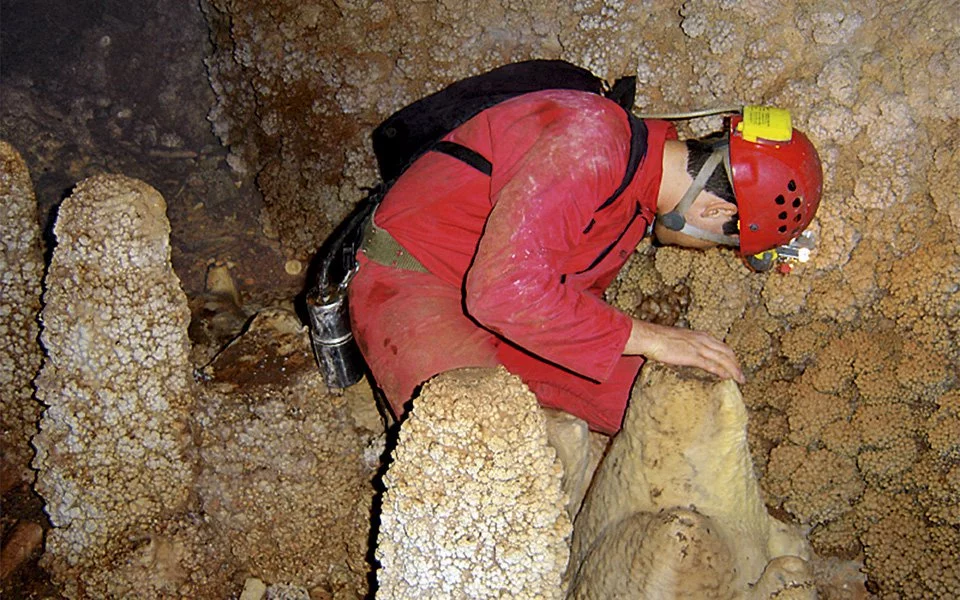
The Petralona Cave is a true marvel of nature, spanning an impressive surface area of 10,400 square meters and filled with an array of stunning geological formations. The cavern is known as the “red-rock cave” due to the vibrant bauxite deposits that give the stone its distinctive hue, creating a breathtaking visual spectacle.
Within the cave, visitors are greeted by a dazzling display of stalactites, stalagmites, curtains, shields, and columns, each one a testament to the slow, methodical work of nature over the course of a million years. These intricate formations, sculpted by the dripping of water and the deposition of minerals, offer a window into the ancient geological processes that have shaped the landscape of Greece.
The Paleontological Treasure Trove
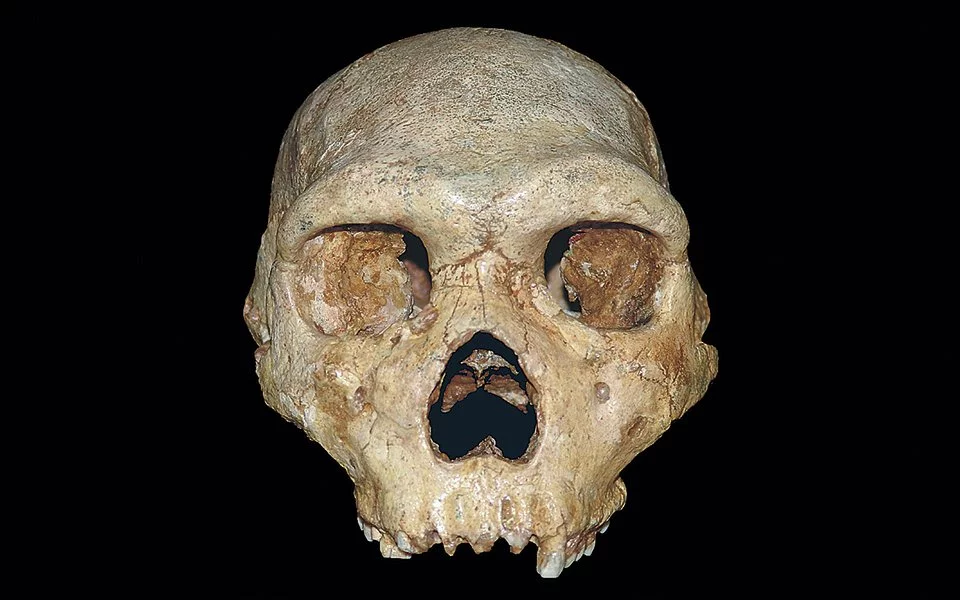
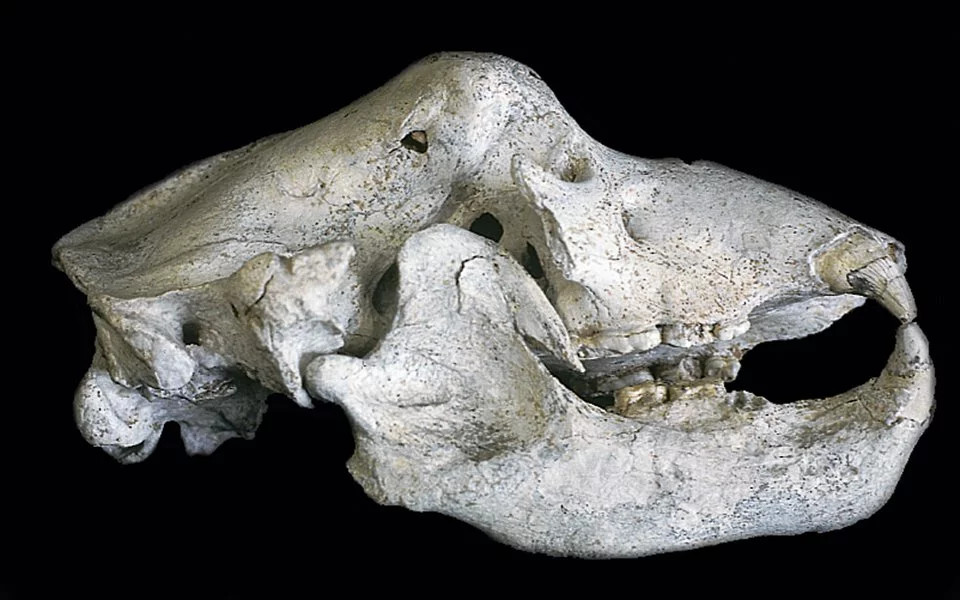
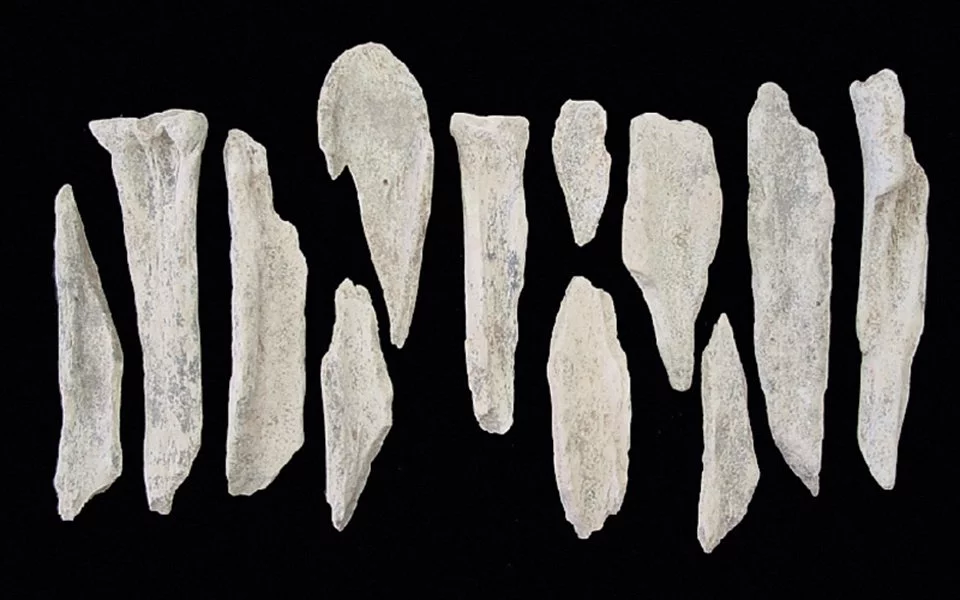
The true significance of the Petralona Cave, however, lies in its remarkable paleontological finds. The site has become known as the “Parthenon of paleontology” due to the sheer abundance and diversity of fossils discovered within its walls. Researchers have unearthed the remains of over 22 different species, including extinct bears, lions, and hyenas, providing invaluable insights into the ancient ecosystem that once thrived in this region.
The most remarkable discovery, however, was the fossilized human skull found in 1960. This ancient cranium, estimated to be around 200,000 years old, represents one of the oldest human remains ever discovered in Greece and has become a crucial piece in the puzzle of human evolution. The physical features of the skull suggest that it belonged to an individual transitioning from Homo erectus to Homo sapiens, offering a glimpse into the complex and fascinating story of our species’ origins.
The Anthropological Museum and Ongoing Research
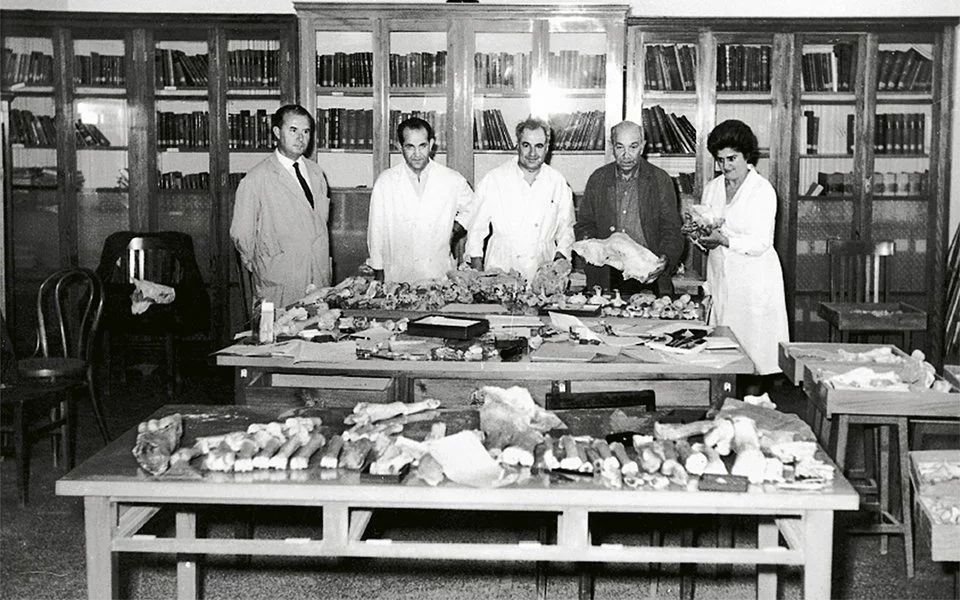
Complementing the natural wonders of the Petralona Cave is the nearby Anthropological Museum, a 1,000-square-meter structure that houses an impressive collection of fossils and artifacts from the site and other archaeological investigations in the region. Visitors can explore the museum’s 400 exhibit cases, which showcase not only the Petralona Skull but also a wealth of large mammal fossils, stone and bone tools, and other fascinating finds.
The Petralona Cave and its associated museum continue to be the focus of intense scientific research, as researchers from around the world collaborate to unravel the secrets of this remarkable site. Dr. Evangelia Tsoukala, a professor at Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and one of the researchers who has examined the items recovered from the cave, notes that the region is “continuously producing fossils,” with new discoveries being made all the time.
The Significance of the Petralona Cave

The Petralona Cave and its remarkable discoveries hold immense significance for our understanding of Greece’s prehistoric past and the evolution of our species. The fossilized human skull, in particular, has become a touchstone for paleoanthropologists, who have studied it extensively in an effort to unravel the mysteries of human origins.
Beyond its scientific importance, the Petralona Cave also serves as a testament to the incredible natural wonders that lie hidden within Greece’s landscapes. The intricate geological formations and the wealth of fossil remains offer a glimpse into a bygone era, allowing us to connect with the ancient world and gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of life that has unfolded over millennia.
Conclusion

The Petralona Cave is a true gem of Greece’s natural heritage, a window into the prehistoric past that continues to captivate and inspire the scientific community. From its remarkable geological formations to its groundbreaking paleontological discoveries, this remarkable site has become a symbol of the country’s enduring connection to its ancient roots.
As we continue to explore and unravel the secrets of the Petralona Cave, we can only imagine the insights and revelations that await us. Whether you are a student of history, a lover of nature, or simply curious about the mysteries of the past, a visit to this extraordinary site is sure to leave a lasting impression, igniting a sense of wonder and a deeper appreciation for the incredible story of our shared human heritage.
