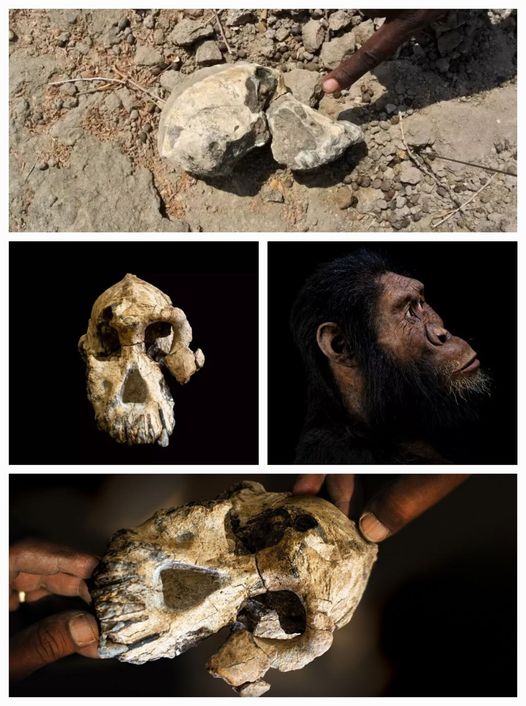
The field of paleoanthropology has long been captivated by the evolutionary history of our early human ancestors. Recently, a remarkable discovery in Ethiopia has shed new light on this intriguing aspect of our past. Researchers have unearthed a “remarkably complete” skull belonging to the early human ancestor, Australopithecus anamensis, providing a tantalizing glimpse into the face of our possible forebears.
The Remarkable Discovery

In 2016, researchers working on the Woranso-Mille Paleoanthropological Research Project in the Afar Regional State of Ethiopia made an extraordinary find. After 15 years of meticulous work in the region, they discovered the upper jaw of an early human ancestor. Determined to uncover more, the team spent 16 hours scouring the area and were rewarded with the recovery of the rest of the skull, now referred to as MRD.
Insights into Australopithecus anamensis
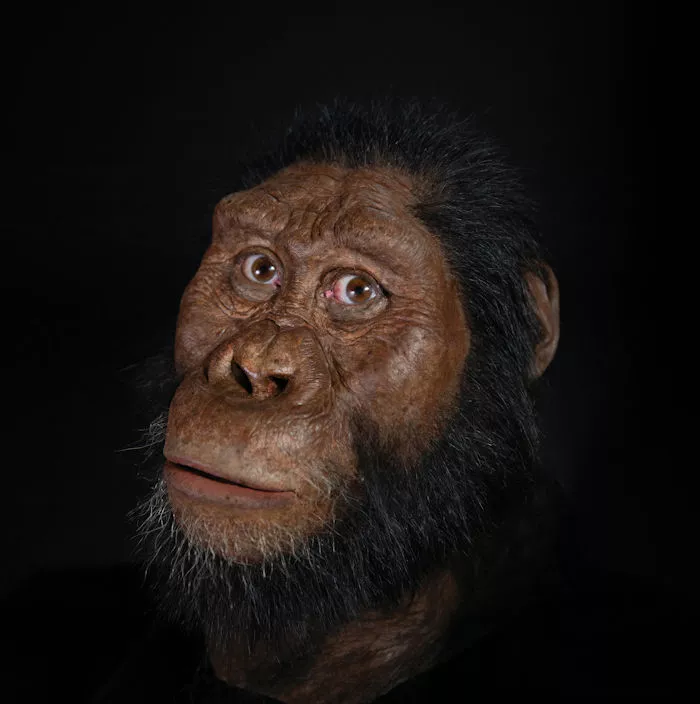

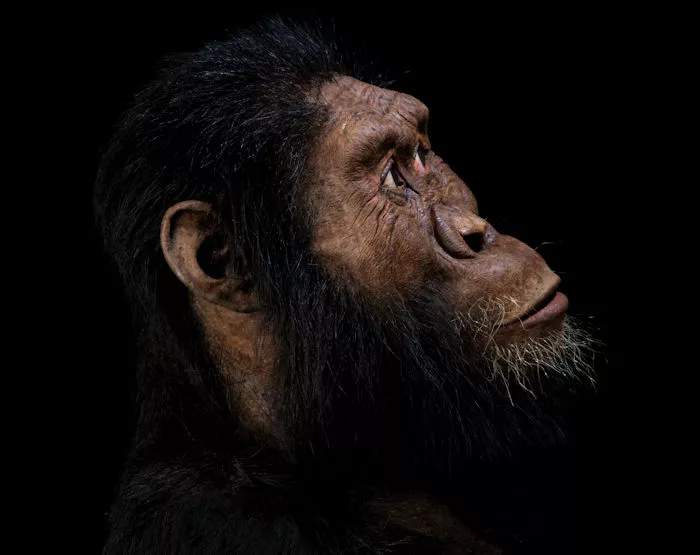
The MRD skull represents the early human ancestor known as Australopithecus anamensis, who lived between 3.9 and 4.2 million years ago. This species is believed to be the ancestor of the famous Lucy skeleton, which belonged to Australopithecus afarensis. The discovery of the MRD skull has challenged the traditional linear view of human evolution, revealing that the two species likely co-existed for at least 100,000 years.
A Mosaic of Primitive and Derived Features
The MRD skull, which belonged to a male, displays a fascinating blend of primitive and more advanced characteristics. It has a protruding face and prominent cheekbones, reflecting the masticatory demands of its diet. However, the skull also shows early signs of the evolutionary transition towards a more human-like facial structure, foreshadowing the changes that would come with the emergence of the genus Homo.
Bridging the Evolutionary Gap
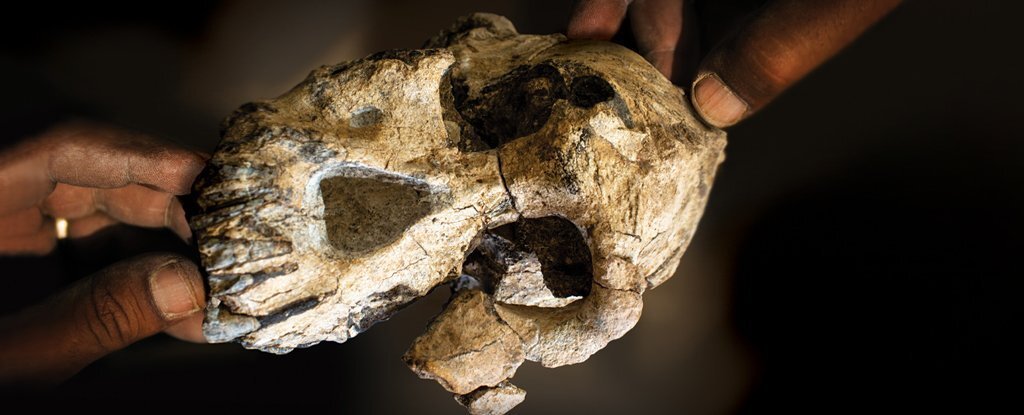
The discovery of the MRD skull is particularly significant as it helps to fill the gap between the earliest known human ancestors, which date back around six million years, and the more recent species like Lucy, which are two to three million years old. This new find provides a crucial link in the evolutionary puzzle, allowing researchers to better understand the morphological changes that occurred during this crucial period.
The Significance of the Discovery
The unearthing of the 3.8-million-year-old Australopithecus anamensis skull in Ethiopia has sent shockwaves through the scientific community. This remarkable discovery not only sheds light on the face of our possible ancestors but also challenges long-held assumptions about the linear nature of human evolution. As researchers delve deeper into the insights provided by this fossil, the evolutionary story of our species continues to unfold, revealing the intricate tapestry of our past.
The Ongoing Pursuit of Knowledge
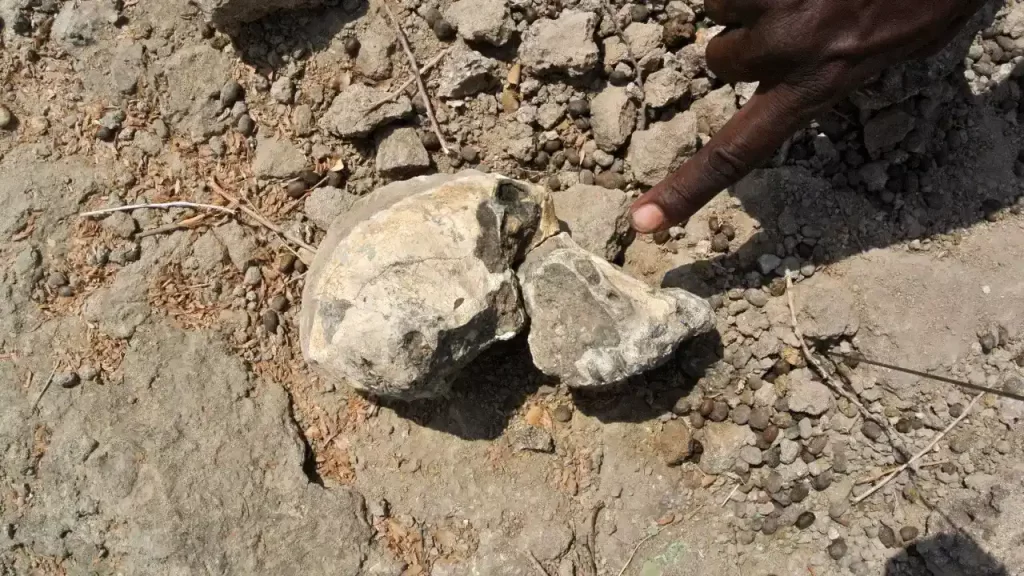

The discovery of the MRD skull is a testament to the dedication and perseverance of the researchers involved in the Woranso-Mille Paleoanthropological Research Project. Their meticulous work over the course of 15 years has yielded a remarkable find that has the potential to transform our understanding of human evolution.
As the scientific community continues to analyze and study the MRD skull, we can expect to gain even deeper insights into the lives and adaptations of our early human ancestors. This discovery represents a significant step forward in our quest to uncover the mysteries of our past and better understand the evolutionary journey that has led to the modern human species.
Conclusion
The discovery of the Australopithecus anamensis skull in Ethiopia has captivated the scientific community and the public alike. This remarkable find not only provides a glimpse into the face of our possible ancestors but also challenges our understanding of the linear nature of human evolution. As researchers continue to explore the insights offered by this fossil, the evolutionary story of our species will continue to unfold, revealing the intricate tapestry of our past and the remarkable adaptations that have shaped us into the humans we are today.
